North Korean hackers unleashed Chrome 0-day exploit on hundreds of US targets
[ad_1]

Getty Photos
Hackers backed by North Korea’s authorities exploited a crucial Chrome zero-working day in an endeavor to infect the computer systems of hundreds of individuals operating in a vast variety of industries, together with the news media, IT, cryptocurrency, and fiscal products and services, Google explained Thursday.
The flaw, tracked as CVE-2022-0609, was exploited by two individual North Korean hacking groups. The two teams deployed the same exploit kit on websites that either belonged to legit organizations and had been hacked or were being established up for the convey purpose of serving assault code on unsuspecting guests. One group was dubbed Operation Aspiration Job, and it targeted additional than 250 individuals doing work for 10 different providers. The other group, recognized as AppleJeus, targeted 85 people.
Dream careers and cryptocurrency riches
“We suspect that these groups work for the identical entity with a shared supply chain, that’s why the use of the exact exploit package, but every single function with a different mission set and deploy various approaches,” Adam Weidemann, a researcher on Google’s danger investigation team, wrote in a put up. “It is achievable that other North Korean governing administration-backed attackers have obtain to the identical exploit package.”
Procedure Dream Position has been lively considering the fact that at minimum June 2020, when researchers at stability firm ClearSky noticed the team focusing on defense and governmental providers. Undesirable men targeted distinct staff members in the businesses with bogus offers of a “aspiration job” with businesses these as Boeing, McDonnell Douglas, and BAE. The hackers devised an elaborate social-engineering campaign that employed fictitious LinkedIn profiles, email messages, WhatsApp messages, and telephone calls. The intention of the campaign was equally to steal income and accumulate intelligence.
AppleJeus, in the meantime, dates back again to at the very least 2018. Which is when researchers from safety agency Kaspersky noticed North Korean hackers focusing on a cryptocurrency trade utilizing malware that posed as a cryptocurrency buying and selling software.
The AppleJeus procedure was noteworthy for its use of a destructive app that was published for macOS, which organization researchers explained was most likely the initially time an APT—short for federal government-backed “advanced persistent risk group”—used malware to target that platform. Also noteworthy was the group’s use of malware that ran solely in memory devoid of composing a file to the really hard generate, an innovative attribute that tends to make detection much more challenging.
One particular of the two groups (Weidemann did not say which one) also employed some of the similar management servers to infect protection researchers previous yr. The marketing campaign utilised fictitious Twitter personas to establish relationships with the researchers. At the time a level of rely on was recognized, the hackers employed both an Online Explorer zero-working day or a destructive Visual Studio challenge that purportedly contained resource code for a proof-of-idea exploit.
In February, Google researchers realized of a important vulnerability getting exploited in Chrome. Company engineers set the vulnerability and gave it the designation CVE-2022-0609. On Thursday, the enterprise furnished much more specifics about the vulnerability and how the two North Korean hackers exploited it.
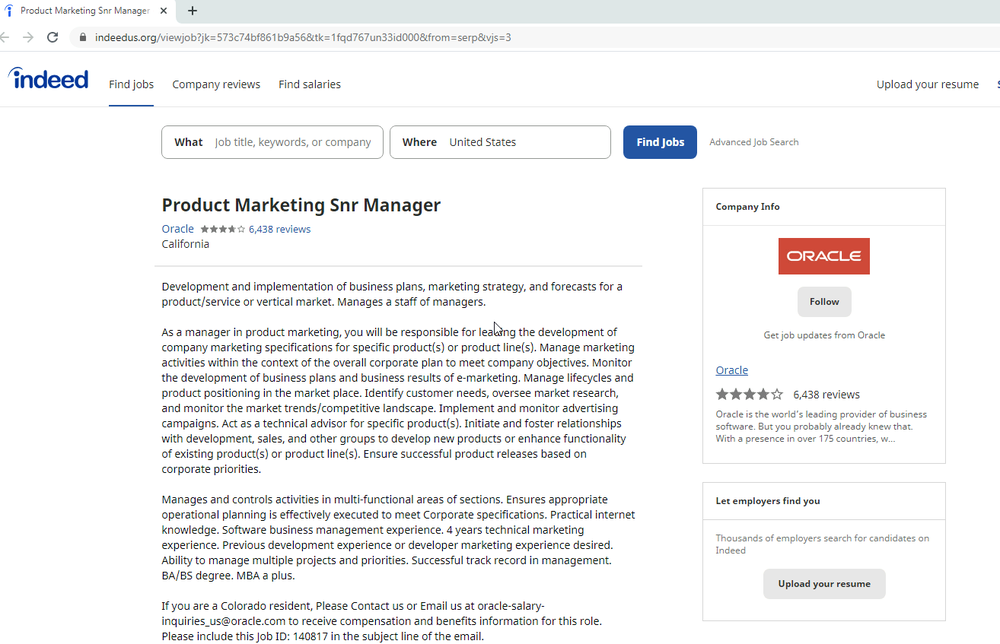
Operation Desire Task despatched targets email messages that purported to arrive from work recruiters doing the job for Disney, Google, and Oracle. One-way links embedded into the e mail spoofed authentic career searching sites these types of as Certainly and ZipRecruiter. The websites contained an iframe that brought on the exploit.
Here’s an instance of 1 of the internet pages applied:
Users of Procedure AppleJeus compromised the websites of at minimum two reputable fiscal solutions providers and a selection of advertisement hoc web-sites pushing destructive cryptocurrency apps. Like the Desire Task web sites, the web sites used by AppleJeus also contained iframes that triggered the exploit.
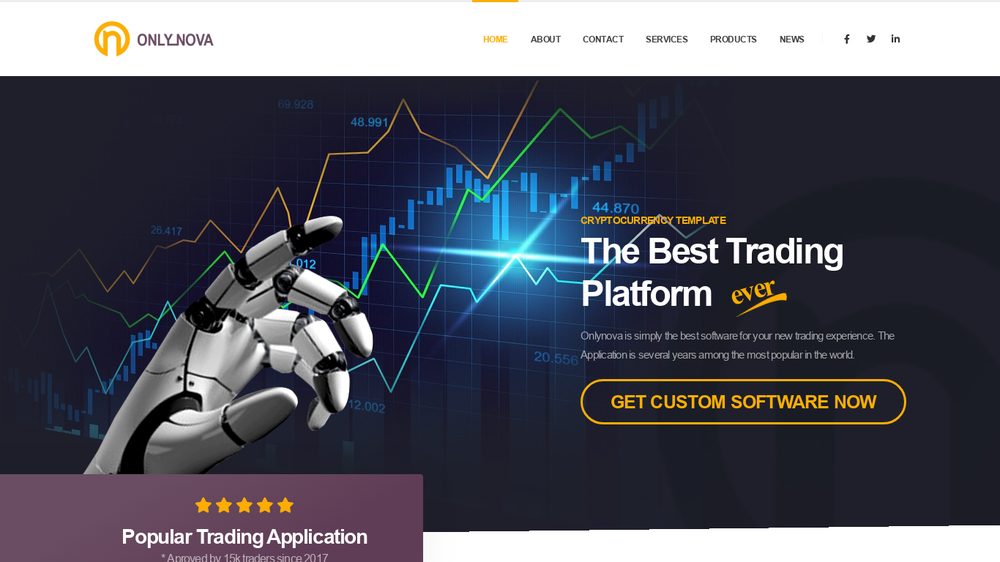
A phony application pushed in Procedure AppleJeus
Is there a sandbox escape in this package?
The exploit package was written in a way to thoroughly conceal the attack by, amongst other issues, disguising the exploit code and triggering distant code execution only in pick scenarios. The kit also appears to have used a separate exploit to crack out of the Chrome safety sandbox. The Google researchers were unable to decide that escape code, leaving open up the likelihood that the vulnerability it exploited has nevertheless to be patched.
[ad_2]
Resource hyperlink
